What is Application Programming Interface? How Does it Work?
An Application Programming Interface (API) acts as a bridge between systems. It allows two or more applications to communicate with each other. APIs let one application (the client) send requests to another (the server). In return, the server sends a response based on that request.
This interaction allows data to be shared and supports feature enhancement. For example, a mobile app might use APIs to access data stored in the cloud. Through APIs, services work together without exposing internal logic.
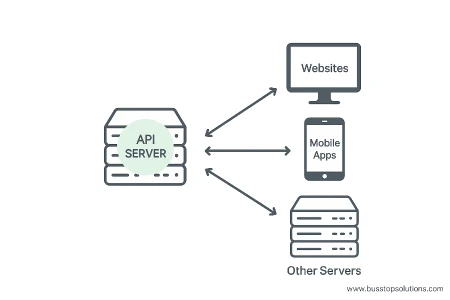
What Are the Use Cases of API?
APIs are used in almost every modern software solution. They support communication, data access, and service integration. Common API use cases include:
- Banking Transactions: Secure connections between systems for fast and safe money transfers.
- Mobile Applications: Fetch user data or updates by interacting with backend systems.
- Hardware Integration: Control smart devices or sensors via software platforms.
- System Integrations: Connect multiple platforms and sync their features or data.
APIs allow developers to build modular systems that scale easily. They promote faster development by reusing existing services and components.
Types of APIs
APIs come in different types, each with unique protocols and use cases. Main API types include:
- REST APIs: Most popular. They use HTTP methods and return lightweight JSON responses.
- SOAP APIs: Strict and secure. Ideal for enterprise apps with structured data needs.
- GraphQL: Flexible and efficient. Clients request only the data they need.
- RPC APIs: Fast and direct. Useful for high-performance, real-time applications.
Choosing the right API depends on the system’s needs and the data format preferred.
Configuration Parameters
Every API request has several configuration components. These help the server understand what the client wants. The key parts include:
- Endpoint: The specific URL where a resource is located.
- Header: Metadata like data type, auth tokens, or content language.
- Body: Payload with extra details, like user data or transaction info.
When the server processes a request, it returns a response. This response includes:
1. Status Code: Shows the result of the request:
- 200 OK: Request successful
- 404 Not Found: Resource doesn’t exist
- 500 Internal Server Error: Something failed on the server
2. Response Body: Data requested or message explaining the status
3. Headers: Format and metadata about the response
Where Are APIs Used?
APIs are present across software development, hardware interaction, and service integrations. Popular areas where APIs are used:
- API-Enabled Services: Google Maps API or YouTube API enable custom feature integration.
- Command-Line Utilities: cURL helps developers test API requests via the terminal.
APIs improve productivity by providing reusable, tested building blocks.
Standard Data Formats for APIs
APIs use structured formats to exchange data between systems. These formats ensure that both client and server understand the content. Common data formats include:
- JSON (JavaScript Object Notation): Lightweight and readable. Default for REST APIs.
- XML (eXtensible Markup Language): Hierarchical and strict. Common in SOAP APIs.
Both formats define data clearly so developers can write clean, secure integrations.
Benefits of APIs
APIs deliver value to businesses, developers, and end users. Core advantages include:
- Cross-Platform Communication: Share functionality across mobile, web, and desktop apps
- Faster Development: Developers avoid rebuilding logic already handled by existing APIs.
- Easy Integration: Third-party APIs simplify adding new features, like payments or resumes.
- Broader Reach: One backend powers multiple platforms—apps, websites, or news feeds.
- Improved Security: APIs enforce access controls and protect sensitive data.
With APIs, teams can innovate faster while maintaining a secure and scalable architecture.

